Strong Saudi Economic Fundamentals Driving Facilities Management Upside
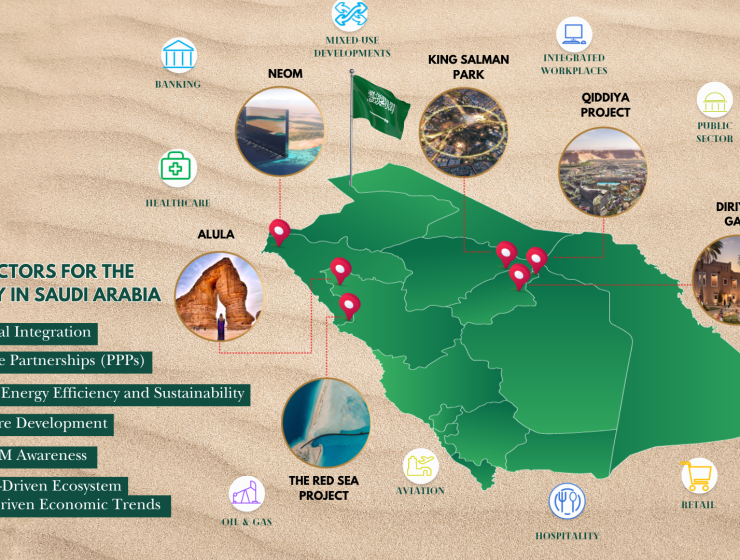
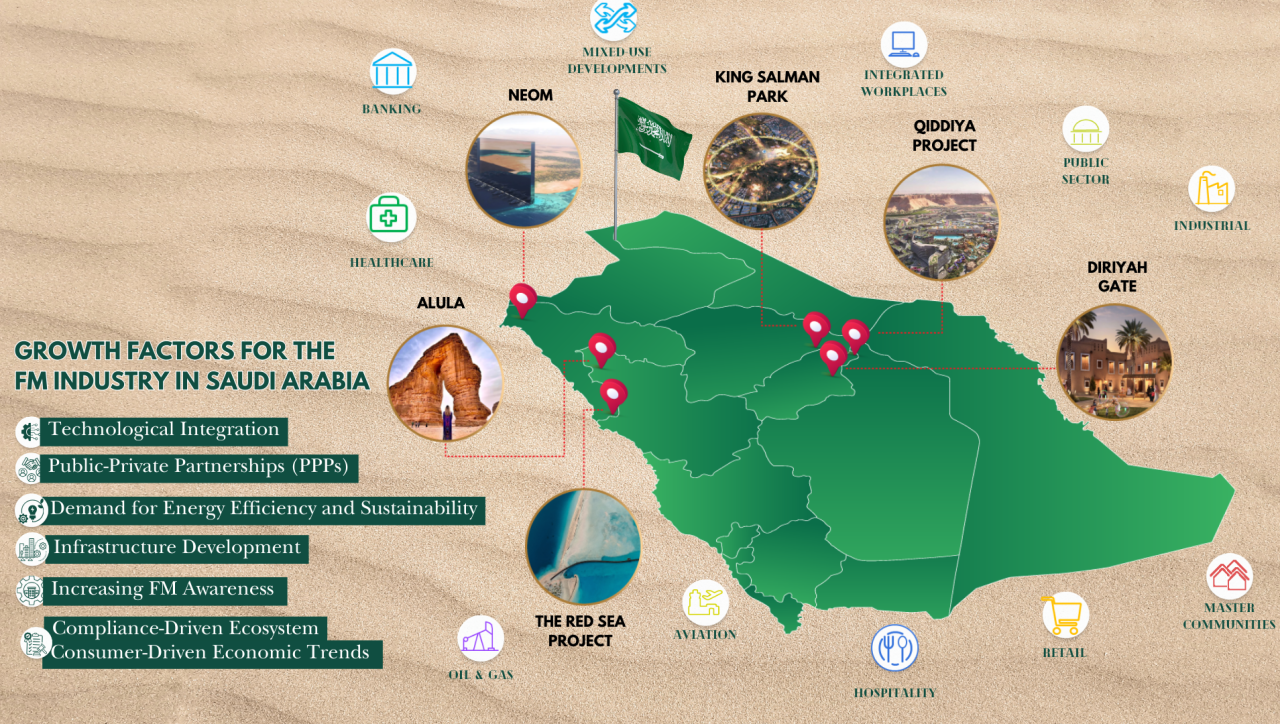
The world is truly mesmerized by Saudi Arabia’s Giga projects, but there is much more, in essence, in the country’s growth footprint beyond these initiatives. Saudi Arabia has indeed successfully adapted to the drive of economic diversity, with many sectors showing a dynamic growth trajectory. Beyond its Giga projects pipeline, the economy has diversified significantly over the years, largely due to its Economic Diversification and Vision 2030 initiatives, which have positively impacted various sectors. Saudi Arabia’s Vision 2030 aims to reduce the nation’s dependence on oil by expanding into tourism, entertainment, and technology sectors. The Kingdom’s Ministry of Finance reported that in 2024, non-oil income accounted for 40% of total government revenues, reaching approximately $134 billion—a 9.78% increase from the previous year. This strategic shift has resulted in increased investments in infrastructure and real estate, which in turn has boosted the demand for services sectors. The facility management (FM) industry in Saudi Arabia is also experiencing significant growth, driven by several key factors. 1. Infrastructure Development: The country is witnessing accelerated urbanization, with substantial investments in large-scale infrastructure projects such as NEOM, Dirriyah, Al Ula, King Salman Park, Qiddiya, and The Red Sea Project. These developments require advanced FM services involving a whole gamut of extensive services to ensure operational efficiency, sustainability, and optimal asset management. 2. Technological Integration: The Kingdom’s nationwide push for e-governance has resulted in a spectacular technological renaissance. The adoption of advanced technologies, including the Internet of Things (IoT) and Artificial Intelligence (AI), is transforming FM operations in Saudi Arabia. These technologies enable real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and energy management, creating increased demand. There is also a rising need for machine and tool automation, particularly robotics, in line with the innovation drive. The integration of advanced technology and the anticipated surge in demand for data centres throughout the Kingdom are expected to boost the need for operations and maintenance services for these centres. 3. Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs): The rise of PPPs in Saudi Arabia signifies a pivotal shift in infrastructure development and management. These collaborations between the government and private entities are driving the demand for FM services as a measure of governance for building asset longevity and maintenance throughout the lifecycle of projects within their PPP frameworks. 4. Demand for Energy Efficiency and Sustainability: There is a growing global emphasis on energy management and sustainability within the FM industry. Saudi, too, is pushing this agenda aligned with their COP pledges and commitments. Many Saudi entities are implementing comprehensive energy efficiency measures. The adoption of energy management programs and technologies that allow for real-time monitoring of energy usage is facilitating informed decision-making and continual improvement in energy efficiency. This focus aligns with global trends toward sustainable development and environmental, social, and governance (ESG) compliance, becoming a significant driver in the Saudi FM market. 5. Consumer-Driven Economic Trends: Sectors such as F&B, retail, education, healthcare, and technology are experiencing upward economic trends, leading to increased spending and spurring growth prospects, opening forays for FM services across malls, restaurants, hospitals and schools. There is a noticeable paradigm shift among clients moving away from conventional maintenance models in favour of Integrated Facility Management (IFM) models. 6. Increasing FM Awareness and Compliance-Driven Ecosystem: The growing awareness of FM in the Saudi market is positively influencing industry prospects. Organizations are recognizing the strategic importance of FM services in enhancing operational efficiency, reducing costs, and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards. This heightened awareness is driving greater demand for both hard and soft FM services across various sectors. In accordance with a recently published report by P&S Intelligence, Saudi Arabian FM market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 12.4% from 2024 to 2030, reaching USD 90.1 billion by 2030, with the organized FM industry expected to be the greatest beneficiary. Large governmental and private entities are actively seeking advanced FM solutions, realizing the growing importance of FM and its impact on compliance, quality, end-user needs, and long-term financial goals. The current buoyant supply chain activity across the Kingdom indicates an increasing demand for FM services, bolstered by the rising awareness among firms regarding corporate real estate management. This trend contributes to the growth of the property service segments with a whole bundle of services, such as workplace solutions. Furthermore, the increasing emphasis on adopting sustainable practices is also expected to impact the demand for FM services positively. In summary, the rising awareness of the benefits of facility management among Saudi organizations is a key driver of the industry’s positive outlook, leading to increased adoption of FM services and contributing to the market’s robust growth projections. Collectively, these factors are propelling the growth of the FM industry in Saudi Arabia, positioning it as a critical component of the national economic transformation and development agenda. The IFM sector has definitely evolved into a sunrise industry, with projections indicating growth rates likely to exceed 15% annually. What is glaring in this growth paradigm is that most of its growth is driven by the shift from conventional operations and maintenance (O&M) to IFM supported by brick-and-mortar sectors like infrastructure development and consumer-driven sectors such as hospitality, retail, and entertainment.